CMSC
-0.0600


One of the world's most storied shipwrecks, Ernest Shackleton's Endurance, has been discovered off the coast of Antarctica more than a century after its sinking, explorers announced Wednesday.
Endurance was discovered at a depth of 3,008 metres (9,869 feet) in the Weddell Sea, about six kilometres (four miles) from where it was slowly crushed by pack ice in 1915.
"We are overwhelmed by our good fortune in having located and captured images of Endurance," said Mensun Bound, the expedition's director of exploration.
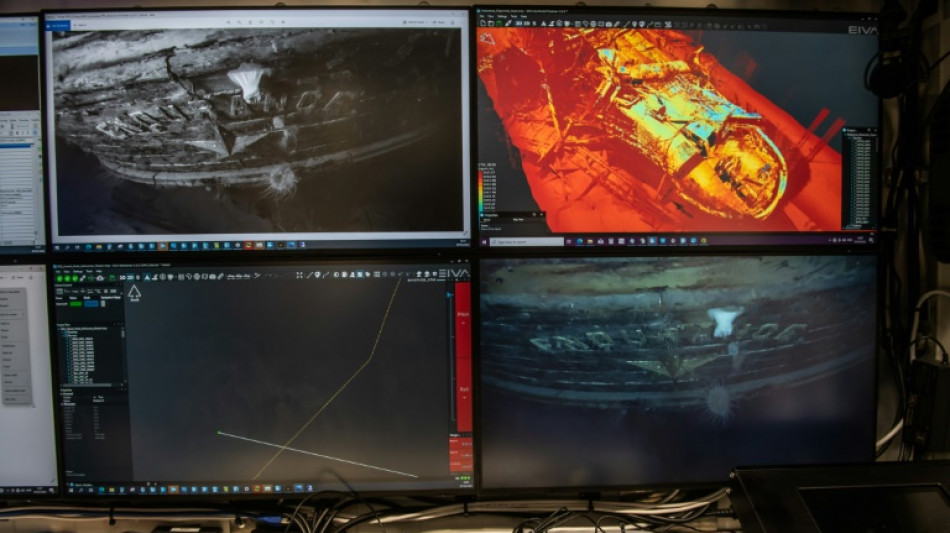
"This is by far the finest wooden shipwreck I have ever seen. It is upright, well proud of the seabed, intact, and in a brilliant state of preservation. You can even see 'Endurance' arced across the stern," he said in a statement.
The expedition, organised by the Falklands Maritime Heritage Trust, left Cape Town on February 5 with a South African icebreaker, hoping to find the Endurance before the end of the Southern Hemisphere summer.
As part of Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic expedition between 1914 and 1917, Endurance was meant to make the first land crossing of Antarctica, but it fell victim to the tumultuous Weddell Sea.
Just east of the Larsen ice shelves on the Antarctic peninsula, it became ensnared in sea-ice for over 10 months before being crushed and sinking.
- 'Worst sea in the world' -
The voyage became legendary due to the miraculous escape Shackleton and his crew made on foot and in boats.
The crew managed to escape by camping on the sea ice until it ruptured.
They then launched lifeboats to Elephant Island and then South Georgia Island, a British overseas territory that lies around 1,400 kilometres east of the Falkland Islands.
Despite the hardships, all of the crew survived.
The explorers used underwater drones to find and film the shipwreck in the merciless Weddell Sea, which has a swirling current that sustains a mass of thick sea ice that can challenge even modern ice breakers.
Shackleton himself described the site of the sink as "the worst portion of the worst sea in the world".
The region remains one of the most difficult parts of the ocean to navigate.
"This has been the most complex subsea project ever undertaken," said Nico Vincent, the mission's subsea project manager.
The underwater drones produced stunningly clear images of the 144-foot-long ship. Amazingly, the helm has remained intact after more than a century underwater, with gear piled against the taffrail as if Shackleton's crew had only recently left it.
The ship's wooden timbers, while damaged from the crush of ice that sank in, still hold together. Sea anemones, sponges and other small ocean life made homes on the wreckage, but did not appear to have damaged it.
Photographs of the expedition showed South Africa's Agulhas II icebreaker surrounded by ice, with crew lifted by crane over the frozen sea.
Under international law, the wreck is protected as a historic site. Explorers were allowed to film and scan the ship, but not to touch it at all -- meaning no artefacts may be returned to the surface.
The team used underwater search drones known as Sabertooths, built by Saab, which dove beneath the ice into the farthest depths of the Weddell Sea.
During the mission, they also researched climate change, documenting ice drifts and weather patterns.
The team is now returning to port in Cape Town.
K.Abe--JT