RBGPF
0.4400


The James Webb space telescope has discovered the oldest black hole ever detected, which was thriving so soon after the Big Bang that it challenges our understanding of how these celestial behemoths form, astronomers said Wednesday.
The black hole was vigorously gobbling up its host galaxy just 430 million years after the birth of the universe during a period called the cosmic dawn, according to a study in the journal Nature.
That makes it 200 million years older than any other massive black hole ever observed, study co-author and Cambridge University astronomer Jan Scholtz told AFP.
Yet it has a mass 1.6 million times greater than our Sun.
Exactly how it had time to grow that big so quickly after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago will provide new information "for the next generation of theoretical models" aiming to explain what creates black holes, Scholtz said.
Like all black holes, it is invisible and can only be detected by the vast explosions of light created when it gobbles up whatever matter is unlucky enough to be nearby.
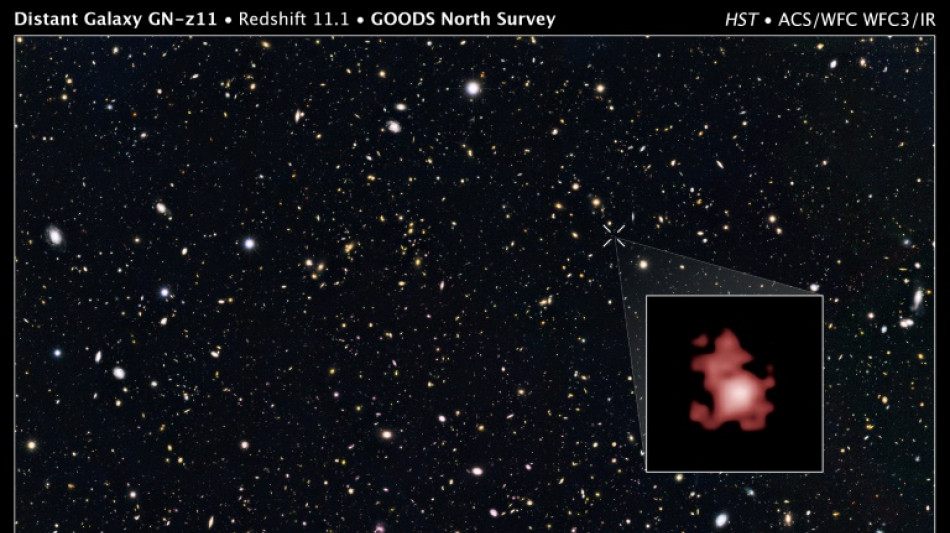
It was this light that allowed the Hubble space telescope in 2016 to spot its host galaxy GN-z11, which is in the direction of the Ursa Major constellation.
At the time GN-z11 was the oldest -- and therefore most distant -- galaxy ever observed. However Hubble did not spot the black hole lurking at its centre.
In 2022, Webb usurped Hubble as the most powerful space telescope, unleashing a torrent of discoveries that have scientists rushing to keep up.
Not only has it spotted the black hole at the heart of GN-z11, but it has also discovered galaxies even further back in time and space, which are also bigger than had been thought possible.
- Growing up fast -
The black hole was energetically eating up GN-z11 during the cosmic dawn, a period which came right after the universe's "dark ages," when stars and galaxies were first born.
It normally takes the supermassive black holes squatting at the centre of galaxies hundreds of millions -- if not billions -- of years to form.
So how could this one have grown so quickly?
Study co-author Stephane Charlot, an astrophysicist at France's Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, suggested that black holes in the early universe could have been formed in a different way than those closer by.
One theory is that they were born huge due to the explosion of especially massive stars that only existed in the early universe, he told AFP.
Or they could have been created by the "direct collapse of a dense gas cloud, without going through the star formation phase," he added.
Once born, the black hole would have been able to gorge itself on the plentiful gas nearby, prompting an almighty growth spurt.
Scholtz emphasised that what has been discovered so far about the black hole of GN-z11 "doesn't rule out any of these scenarios".
And it could be just the beginning.
Scholtz hopes that Webb -- and other telescopes on the way, such as the European Space Agency's Euclid -- will discover more of these black holes in the earliest glimmers of the universe.
K.Nakajima--JT